Human Multi-robot Systems
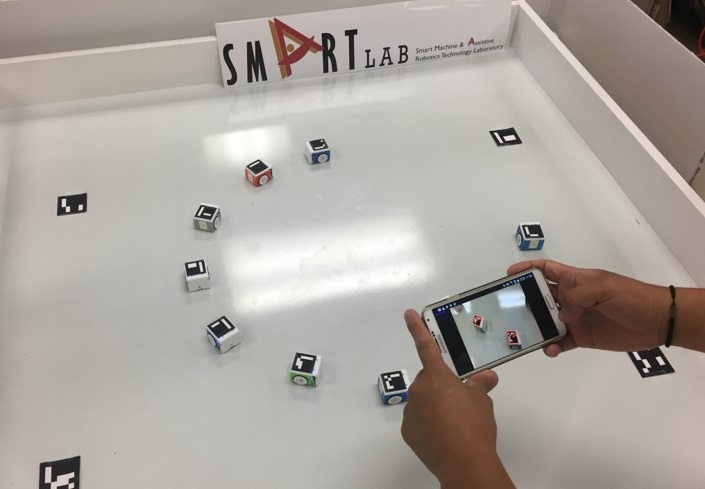
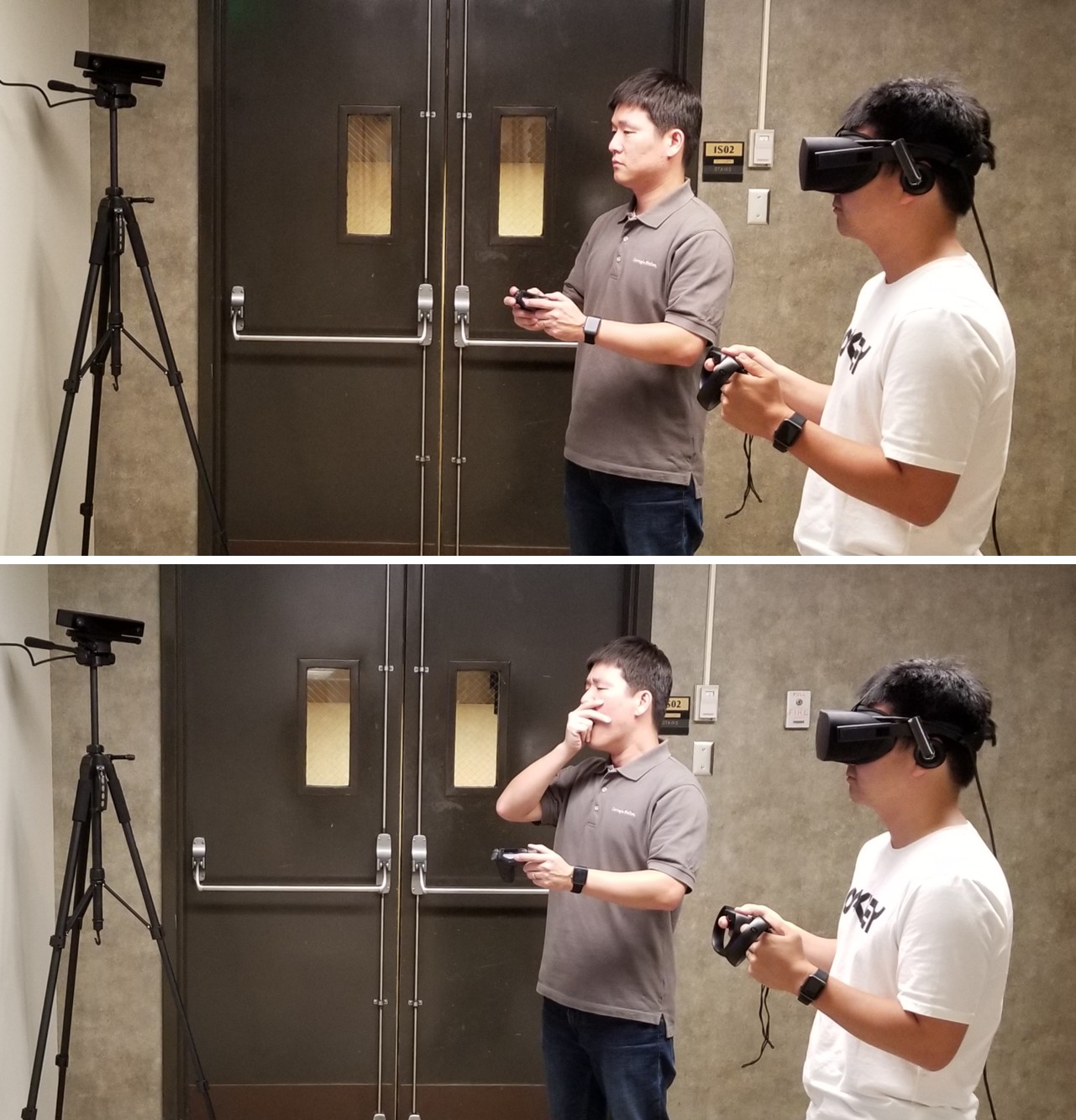


Description: Human multi-robot
systems constitute a relatively new area of research focused
on interaction and collaboration between humans and multiple
robots. Well-designed systems can enable a team of humans and
robots to effectively work together on complex and
sophisticated tasks such as exploration, monitoring, and
search and rescue operations. The SMART lab has accumulated
considerable knowledge in this area while studying multi-robot
systems and robot swarms, human-robot interactions, and
assistive technology/robotics. Currently, we design algorithms
and systems to enable multiple robots to collaborate with each
other in a distributed way and flexibly interact with any
humans, in any situation, anywhere; we also develop
applications that can leverage the advantages of human
multi-robot systems. Through this research, we anticipate a
future where anyone (e.g. people without any experience in
robot control, or people with disabilities) and robots (few or
countless) can work together on various practical tasks.
Grant: NSF
People: Wonse
Jo, Go-Eum
Cha, Ruiqi
Wang, Jeremy
Pan, Revanth Krishna Senthilkumaran
Project Website: https://polytechnic.purdue.edu/ahmrs
Selected Publications:
- Go-Eum Cha and Byung-Cheol Min, "Correlation between Unconscious Mouse Actions and Human Cognitive Workload", 2022 ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems - Late-Breaking Work, New Orleans, LA, USA, April 30–May 6, 2022. Paper Link, Video Link
- Wonse Jo, Robert Wilson, Jaeeun Kim, Steve McGuire, and Byung-Cheol Min, "Toward a Wearable Biosensor Ecosystem on ROS 2 for Real-time Human-Robot Interaction Systems", 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Workshop on HMRS 2021: Cognitive and Social Aspects of Human Multi-Robot Interaction, Prague, Czech Republic, Sep 27 – Oct 1, 2021. Paper Link, Video Link, GitHub Link
- Wonse Jo, Shyam Sundar Kannan, Go-Eum Cha, Ahreum Lee, and Byung-Cheol Min, "ROSbag-based Multimodal Affective Dataset for Emotional and Cognitive States", 2020 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC), Toronto, Canada, 11-14 October, 2020. Paper Link
- Tamzidul Mina, Shyam Sundar Kannan, Wonse Jo, and
Byung-Cheol Min, "Adaptive Workload Allocation for
Multi-human Multi-robot Teams for Independent and
Homogeneous Tasks", IEEE Access, Vol. 8, pp. 152697-152712,
2020. Paper Link, Video Link
Robot Learning
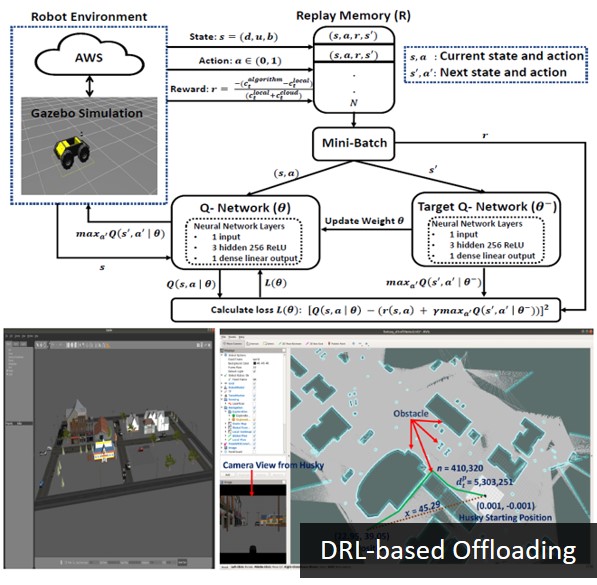
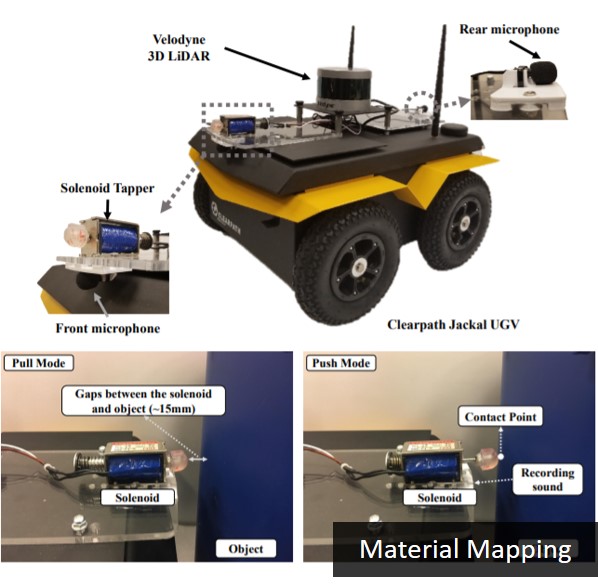
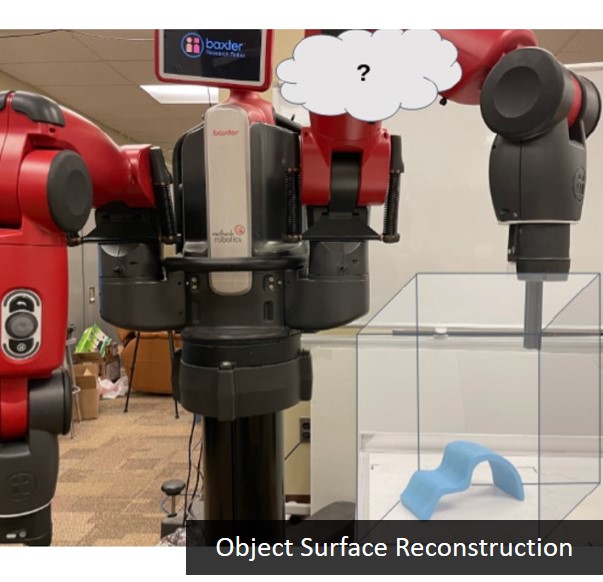
Description: Machine learning is a
field of artificial intelligence focused on algorithms that
allow computers to learn, and has come to receive tremendous
attention from the entire scientific community. Within this
field, the SMART lab focuses on advanced deep learning and
deep reinforcement learning methods with the goal of making
robots more intelligent. We are specifically studying two
major areas in detail. First, we study cognitive computing
methods that model and learn the capacity for fast and
accurate decision-making characteristic of humans, the
better to improve decision-making by robots. Second, we
study recognition technology so as to enable robots to
recognize and judge the identity of an object/scene in
real-time with facility equivalent to humans, even when
faced with dynamic environments and limited information. We
currently aim to apply our developments to diverse
applications including navigation of autonomous robots/cars
in dynamic environments, detection of malware/cyberattacks,
prediction of the cognitive and affective states of humans,
and allocating workloads within human-robot teams.
Grants: NSF, Purdue University
People: Wonse
Jo, Shyam
Sundar Kannan, Su
Sun, Go-Eum
Cha, Vishnunandan
Venkatesh, Ruiqi
Wang
Selected Publications:
- Ruiqi Wang, Weizheng Wang, and Byung-Cheol Min, "Feedback-efficient Active Preference Learning for Socially Aware Robot Navigation", 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2022), Kyoto, Japan, October 23-27, 2022. Paper Link, Video Link, GitHub Link
- Su Sun and Byung-Cheol Min, "Active Tapping via Gaussian Process for Efficient Unknown Object Surface Reconstruction", 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Workshop on RoboTac 2021: New Advances in Tactile Sensation, Interactive Perception, Control, and Learning. A Soft Robotic Perspective on Grasp, Manipulation, & HRI, Prague, Czech Republic, Sep 27 – Oct 1, 2021. Paper Link
- Manoj Penmetcha and Byung-Cheol Min, "A Deep Reinforcement Learning-based Dynamic Computational Offloading Method for Cloud Robotics", IEEE Access, Vol. 9, pp. 60265-60279, 2021. Paper Link, Video Link
- Shyam Sundar Kannan, Wonse Jo, Ramviyas Parasuraman, and Byung-Cheol Min, "Material Mapping in Unknown Environments using Tapping Sound", 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2020), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25-29 October, 2020. Paper Link, Video Link
Water Quality Monitoring and Sediment Sampling
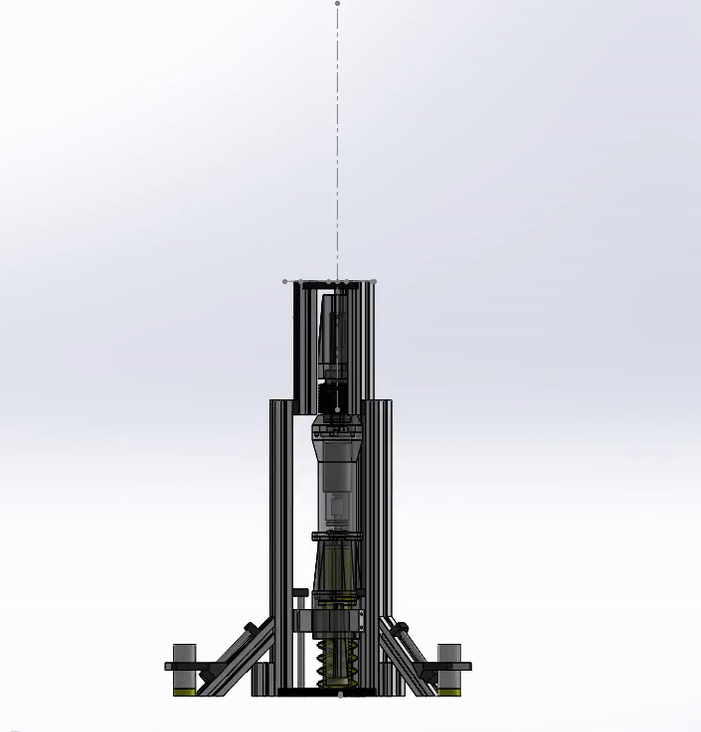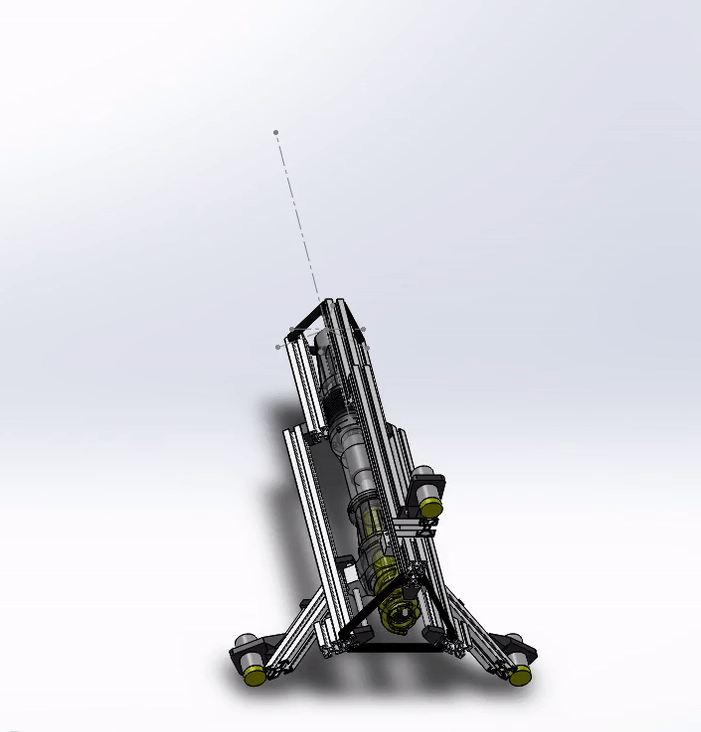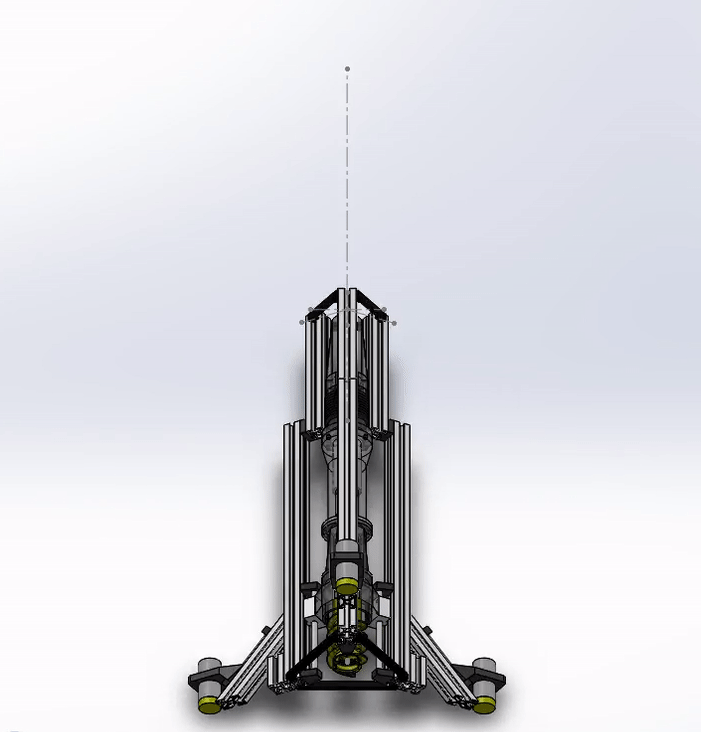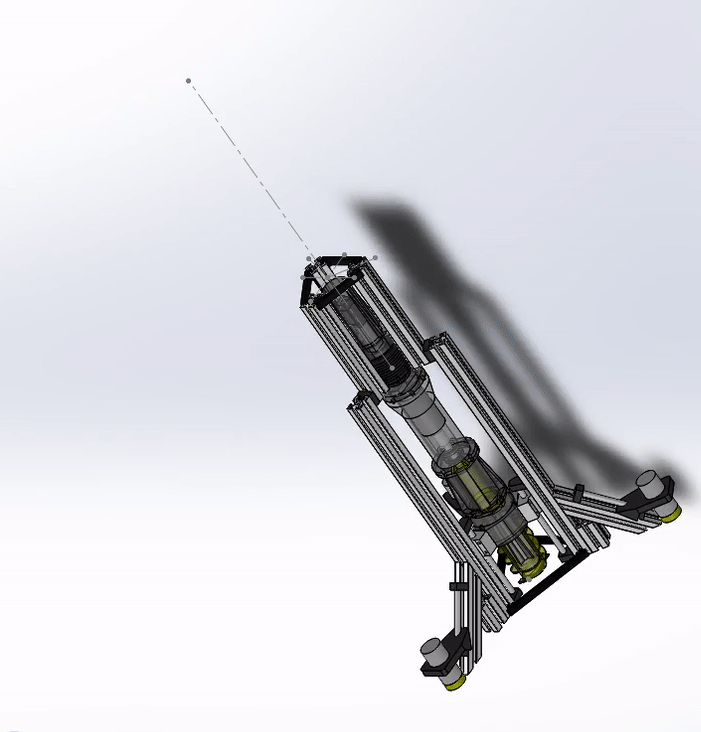
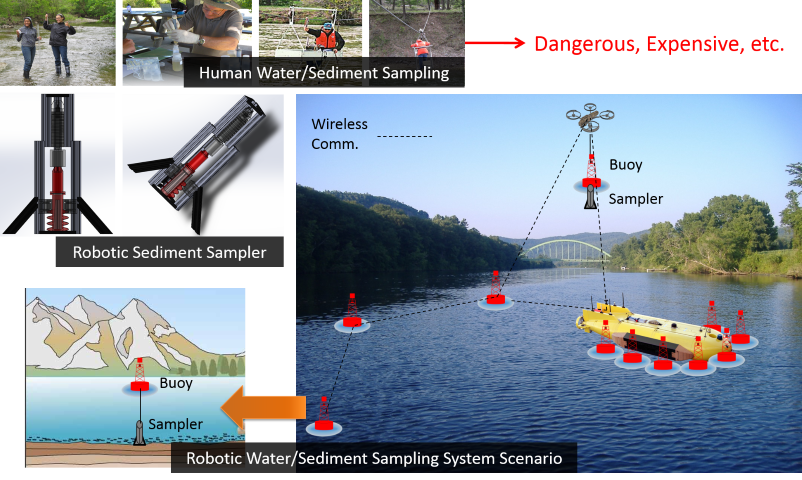
Description: All life depends on
water, and we are all citizens of watersheds; however, human
activities often lead to contamination that can disrupt and
disorganize both biological and social communities.
Moreover, contamination of sediments with pollutants such as
heavy metals can damage habitats for fish and other aquatic
life, and even affect human health. Belated recognition of a
water crisis can incur tremendous costs and require
considerable recovery time, and also foster social and
political strife. As such, there is great benefit in regular
monitoring of water and sediment quality through sampling
activities. The SMART lab is currently developing a novel
cyber-physical system for water and sediment sampling,
integrating control software and mobile robots to conduct
autonomous monitoring and analysis. Overall, our research
will increase knowledge of how to effectively sample water
and sediments with robotic systems and verify the ability of
cyber-physical systems to enable real-time data processing
when monitoring water quality. We believe these
contributions will significantly enhance the
state-of-the-art in robotic environmental monitoring.
Grants: NSF, UNSA, Purdue University
People: Wonse
Jo, Pou
Hei Chan
Project Website: https://engineering.purdue.edu/PRWQ
Selected Publications:
- Jun Han Bae, Wonse Jo, Jee Hwan Park, Richard M. Voyles, Sara K. McMillan and Byung-Cheol Min, "Evaluation of Sampling Methods for Robotic Sediment Sampling Systems", IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, Vol. 46, No. 2, pp. 542-554, April 2021. Paper Link, Video Link
- Jun Han Bae, Shaocheng Luo, Shyam Sundar Kannan, Yogang Singh, Bumjoo Lee, Richard M. Voyles, Mauricio Postigo-Malaga, Edgar Gonzales Zenteno, Lizbeth Paredes Aguilar, and Byung-Cheol Min, "Development of an Unmanned Surface Vehicle for Remote Sediment Sampling with a Van Veen Grab Sampler", 2019 MTS/IEEE OCEANS, Seattle, WA, USA, October 27-31, 2019. Paper Link, Video Link
- Wonse Jo, Jee Hwan Park, Yuta Hoashi, and Byung-Cheol Min, "Development of an Unmanned Surface Vehicle for Harmful Algae Removal", 2019 MTS/IEEE OCEANS, Seattle, WA, USA, October 27-31, 2019. Paper Link, Video Link
- Shaocheng Luo, Yogang Singh, Hanyao Yang, Jun Han Bae, J. Eric Dietz, Xiumin Diao, and Byung-Cheol Min, "Image Processing and Model-Based Spill Coverage Path Planning for Unmanned Surface Vehicles", 2019 MTS/IEEE OCEANS, Seattle, WA, USA, October 27-31, 2019. Paper Link
- Wonse Jo, Yuta Hoashi, Lizbeth Leonor Paredes Aguilar,
Mauricio Postigo-Malaga, José Garcia-Bravo, and
Byung-Cheol Min, "A Low-cost and Small USV Platform for
Water Quality Monitoring", HardwareX, Vol. 6, e00076,
October 2019. Paper Link, Source Codes Link, Video Link
Low-cost and Open-source Robot Platforms
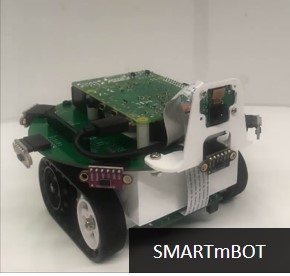
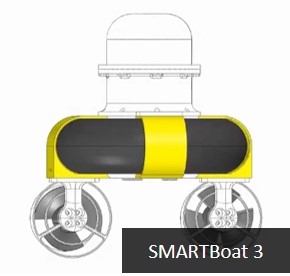
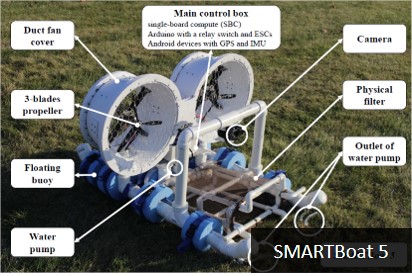
Description: Low-cost,
open-source-based robotic platforms have great value and
potential in many respects. For example, they allow
researchers in the robotics field to conduct real
experiments, advancing their research in a more practical
and efficacious way, and they enable K-12 and college
students to participate in hand-on activities and so learn
robotics more effectively. They also offer opportunities for
end users who are interested in robots, but have been priced
out by high costs. However, only a very few low-cost,
open-source robotic platforms are currently available. The
SMART lab is applying software and hardware development
experience accumulated over many years to develop a variety
of robot types, such as mobile and aquatic robots, that are
inexpensive and easy for anyone to build. We share all our
source code and hardware-related materials through online
repositories such as GitHub.
Grants: NSF, UNSA, Purdue University
People: Wonse
Jo, Pou
Hei Chan
Selected Publications:
- Wonse Jo, Jaeeun Kim, and Byung-Cheol Min, "ROS2
Open-Source Swarm Robot Platform: SMARTmBot", 2021
International Conference on Robotics and Automation
(ICRA), Workshop on Robot Swarms in the Real World: From
Design to Deployment - Live Demonstration, Xi'an, China,
May 30 - June 5, 2021. GitHub Link, Video Link
- Jun Han Bae, Shaocheng Luo, Shyam Sundar Kannan, Yogang Singh, Bumjoo Lee, Richard M. Voyles, Mauricio Postigo-Malaga, Edgar Gonzales Zenteno, Lizbeth Paredes Aguilar, and Byung-Cheol Min, "Development of an Unmanned Surface Vehicle for Remote Sediment Sampling with a Van Veen Grab Sampler", 2019 MTS/IEEE OCEANS, Seattle, WA, USA, October 27-31, 2019. Paper Link, Video Link
- Wonse Jo, Jee Hwan Park, Yuta Hoashi, and Byung-Cheol Min, "Development of an Unmanned Surface Vehicle for Harmful Algae Removal", 2019 MTS/IEEE OCEANS, Seattle, WA, USA, October 27-31, 2019. Paper Link, Video Link
- Wonse Jo, Yuta Hoashi, Lizbeth Leonor Paredes Aguilar,
Mauricio Postigo-Malaga, José Garcia-Bravo, and
Byung-Cheol Min, "A Low-cost and Small USV Platform for
Water Quality Monitoring", HardwareX, Vol. 6, e00076,
October 2019. Paper Link, Source Codes Link, Video Link
Delivery Robots
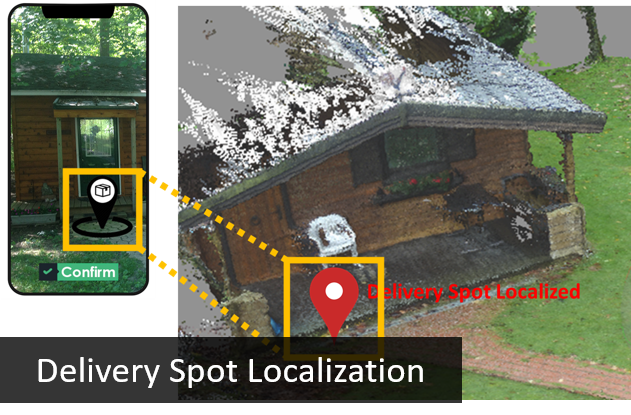


Description: As delivery robots
become more able and also more necessary in delivering goods
both quickly and economically, interest in utilizing robots
for last-mile delivery also increases. However, existing
research endeavors and services involving delivery robots
still remain far from adequate to meet the growing demand in
this area, not to mention far short of being fully
incorporated into our lives. The SMART lab explores various
practical and theoretical topics in robot delivery,
including vehicle routing for drones, localization of a
requested delivery spot, and social interaction between
package recipients and delivery robots. To this end, we use
mathematical methods to tackle optimization problems and
conduct experimental methods based on user studies. We
expect that this research will play a major role in allowing
delivery robots to deliver packages more intelligently and
effectively, like a professional human courier, and that it
will improve human-delivery robot interaction while
increasing robot autonomy.
Grant: Purdue University
People: Shyam Sundar Kannan
Selected Publications:
- Shyam Sundar Kannan and Byung-Cheol Min, "Autonomous Drone Delivery to Your Door and Yard", 2022 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Dubrovnik, Croatia, June 21-24, 2022. Paper Link, Video Link
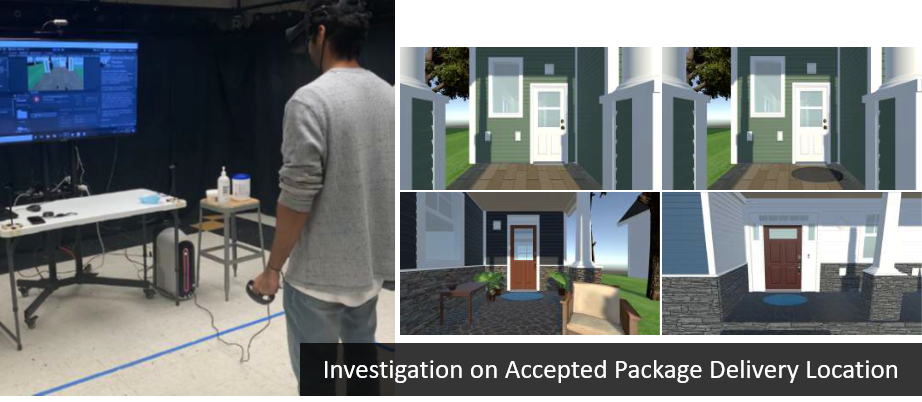
- Shyam Sundar Kannan and Byung-Cheol Min, "Investigation on Accepted Package Delivery Location: A User Study-based Approach", 2021 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Virtual, Melbourne, Australia, 17-20 October, 2021. Paper Link
- Shyam Sundar Kannan, Ahreum Lee, and Byung-Cheol Min, "External Human-Machine Interface on Delivery Robots: Expression of Navigation Intent of the Robot", 2021 30th IEEE International Conference on Robot & Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Virtual, Vancouver, Canada, 8-12 August, 2021. Paper Link, Video Link
- Patchara Kitjacharoenchai, Byung-Cheol Min, and Seokcheon Lee, "Two Echelon Vehicle Routing Problem with Drones in Last Mile Delivery", International Journal of Production Economics, Vol. 25, 2020. Paper Link
