Distributed Rendezvous and Formation Control (2017
- 22)
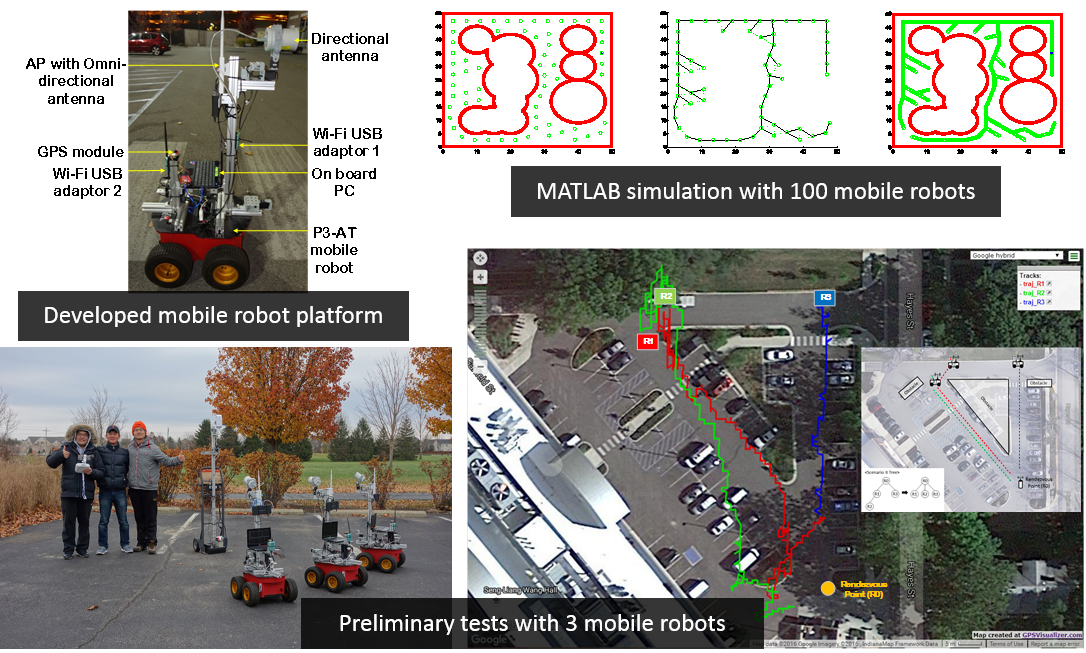
Description: We consider the rendezvous
problem as robots exploring the unknown environment with
minimum communication and arrive at the selected rendezvous
location. The problem of rendezvous is ubiquitous in nature.
Animals in migration are able to share information about food
and water thus the whole group rendezvous at those locations.
Human also have same issue as we need to meet specific people
in specific place, which is applied still in multi-agent
robotic systems. With emerging technologies such as
localization, ubiquitous wireless communication, and advanced
computation capability, enhanced rendezvous control shall
bring wider application scenarios like intelligent warehouse
and urban search and rescue. The purpose of this research is
to develop a bounded distributed rendezvous control mechanism
in cluttered environment. The robots within this environment
have basically none knowledge of the environment, but can
rendezvous at the destination while conquering the limitations
such as communication being blocked by large obstacles, and
path blocked by small obstacles, with proper decision making
mechanism and obstacle avoidance algorithms. Meanwhile, the
efficiency in rendezvous is also considered, we try to figure
out robotic rendezvous control which not only handles
communication unavailable occasions and obstacle avoidance,
but also maintain an efficiency-prior trajectory.
Grants: NSF, Purdue University
People: Shaocheng Luo, Jun Han Bae, Ramviyas Parasuraman
Selected Publications:
- Shaocheng Luo, Jonghoek Kim, and Byung-Cheol Min, "Asymptotic Boundary Shrink Control with Multirobot Systems", IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, Vol. 52, No. 1, pp. 591-605, Jan. 2022. Paper Link, Video Link
- Ramviyas Parasuraman, Jonghoek Kim, Shaocheng Luo, and Byung-Cheol Min, "Multi-Point Rendezvous in Multi-Robot Systems", IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, Vol. 50, Issue 1, pp. 310-323, Jan. 2020. Paper Link, Video Link
- Shaocheng Luo, Jonghoek Kim, Ramviyas Parasuraman, Jun Han Bae, Eric T. Matson, and Byung-Cheol Min, "Multi-robot Rendezvous Based on Bearing-aided Hierarchical Tracking of Network Topology", Ad Hoc Networks, Vol. 86, pp. 131-143, April 2019. Paper Link, Video Link
- Shaocheng Luo, Jun Han Bae, and Byung-Cheol Min, "Pivot-based Collective Coverage Control with a Multi-robot Team", 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (IEEE ROBIO 2018), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, December 12-15, 2018. Paper Link, Video Link
- Ramviyas Parasuraman and Byung-Cheol Min, "Consensus Control of Distributed Robots Using Direction of Arrival of Wireless Signals", International Symposium on Distributed Autonomous Robotic Systems 2018 (DARS 2018), Boulder, CO, USA, Oct 15-17, 2018. Paper Link, Source Codes, Video Link
Reliability and Safety of Autonomous Multi-Agent
Systems (2017 - 21)
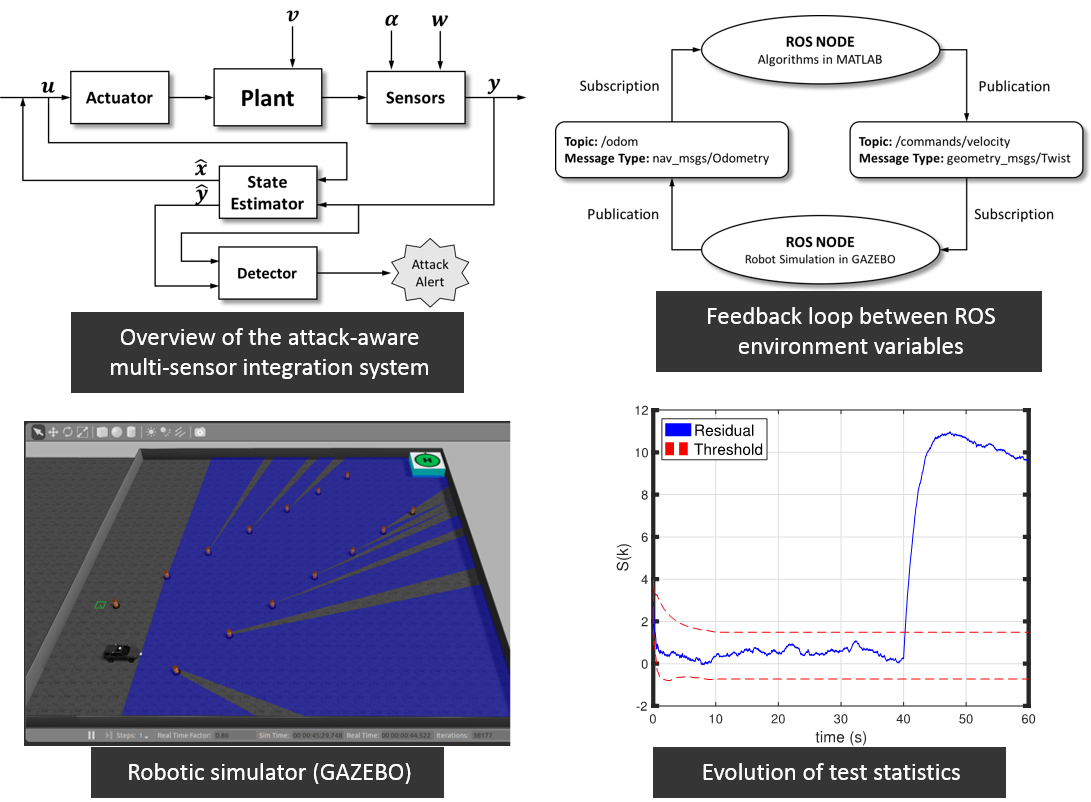
Description: Today's autonomous cars,
otherwise known as driverless vehicles or self-driving cars,
enable the deployment of safety technologies, such as
collision warning, automatic emergency braking, and
Vehicle-to-Vehicle technologies. In the near future, these
systems in all vehicles will help to achieve zero fatalities,
zero injuries, and zero accidents. However, behind the
potential of these innovations, there is new challenge on
autonomous cars that still need to address: cybersecurity.
As the first step, we propose an
attack-aware multi-sensor integration algorithm for the
navigation system. A Fault Detection and Isolation (FDI)
scheme is adopted for the detection of cyberattacks on
navigation systems. Particularly, a discrete Extended Kalman
Filter (EKF) is employed to construct robust residuals in the
presence of noise. The proposed method uses a parametric
statistical tool for detecting attacks based on the residuals
in properties of discrete time signals and dynamic systems. It
is based on a measurement history rather than a single
measurement at a time. These approaches enable the proposed
multi-sensor integration algorithm to generate a quick
detection and low false alarms rate that are suitable to the
applications of dynamic systems. Finally, as a case study,
INS/GNSS integration for autonomous vehicle navigation systems
is considered and tested with software-in-the-loop simulation
(SILS).
In addition, we consider attack detection
algorithms autonomous multi-vehicle systems with imperfect
information. This research addresses how a locally controlled
autonomous agent can be identified by other agents if it has
been compromised and how to make decisions with the ultimate
goal of recovering system functionality and safety.
Grants: NIJ
People: Sangjun Lee
Selected
Publications:
- Sangjun Lee and Byung-Cheol Min, "Distributed Control of Multi-Robot Systems in the Presence of Deception and Denial of Service Attacks", arXiv preprint, arXiv:2102.00098, 2021. Paper Link, Video Link
- Sangjun Lee and Byung-Cheol Min, "Distributed Direction of Arrival Estimation-aided Cyberattack Detection in Networked Multi-Robot Systems", 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2018), Madrid, Spain, October 1-5, 2018. Paper Link, Video Link
- Sangjun Lee, Yongbum Cho, and Byung-Cheol Min, "Attack-aware Multi-sensor Integration Algorithm for Autonomous Vehicle Navigation Systems", 2017 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC), Banff, Canada, 5-8 October, 2017. Paper Link, Video Link
Social Behavior in Multi-robot Systems (2017
- 20)
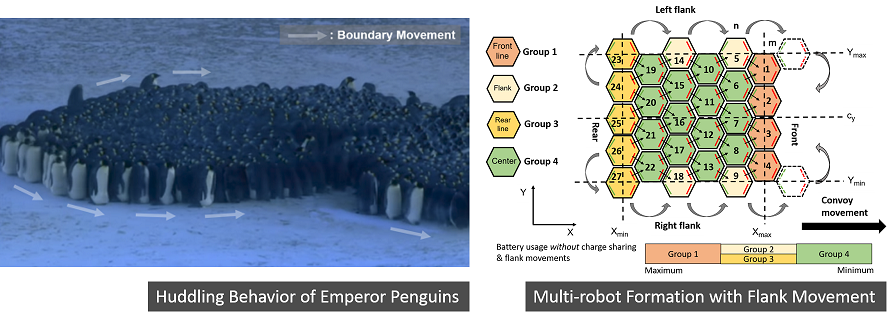
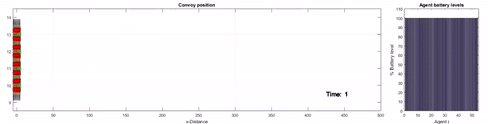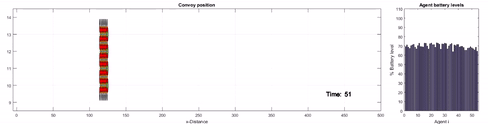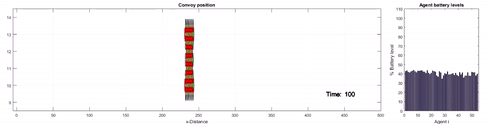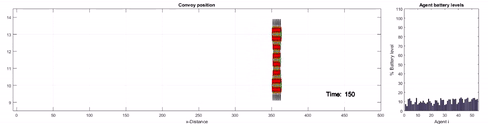
Description: Individuals can benefit in a
social group by looking out for one another for support and
survival. It is a proven phenomenon in nature and in this
research our goal is to apply the same principles in a
multi-robot system to improve robot survivability robustness.
Traditionally, research on multi-robot
systems has focused on developing application specific control
algorithms while adapting individual robots in the group to
operational environments and specific tasks without explicitly
considering the advantages of being in a social group.
However, given the unpredictable nature of various operational
environments and autonomous mission requirements, designing
individual robots that can take into account all possible
scenarios is unfeasible, expensive and still lack robustness
in survivability. In contrast, we believe introducing a social
group aspect to the multi-robot system may provide a unique
and robust way of dealing with such cases.
For our initial work, social behavioral
inspiration was taken from the Huddling behavior of Emperor
Penguins in the Antarctic where they share body heat and take
turns being in the huddle centers to survive conditions as
severe as Antarctic winters as a group.
Potential research on the topic include
energy sharing between heterogeneous robotic agents,
application of machine learning techniques for distributed
position shuffling within the group to survive damaging
external stimuli, distributed control techniques for
cooperative object transportation specifically focusing on
minimal individual health loss for long term survival of the
multi-robot system.
Grants: Purdue University
People: Tamzidul Mina
Selected Publications:
- Tamzidul Mina, Maliha Hossain, Jee Hwan Park, and Byung-Cheol Min, "Efficient Resource Distribution by Adaptive Inter-agent Spacing in Multi-agent Systems", 2019 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC), Bari, Italy, 6-9 October, 2019. Paper Link, Video Link
- Tamzidul Mina and Byung-Cheol Min, "Penguin Huddling Inspired Distributed Boundary Movement for Group Survival in Multi-robot Systems using Gaussian Processes", 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (IEEE ROBIO 2018), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, December 12-15, 2018. Paper Link, Video Link
- Tamzidul Mina and Byung-Cheol Min, "Penguin Huddling-inspired Energy Sharing and Formation Movement in Multi-robot Systems", 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Safety, Security, and Rescue Robotics (SSRR), Philadelphia, PA, USA, August 6-8, 2018. Paper Link, Video Link
A Directional Antenna-based Leader-follower Robotic Convoy System (2013 - 18)
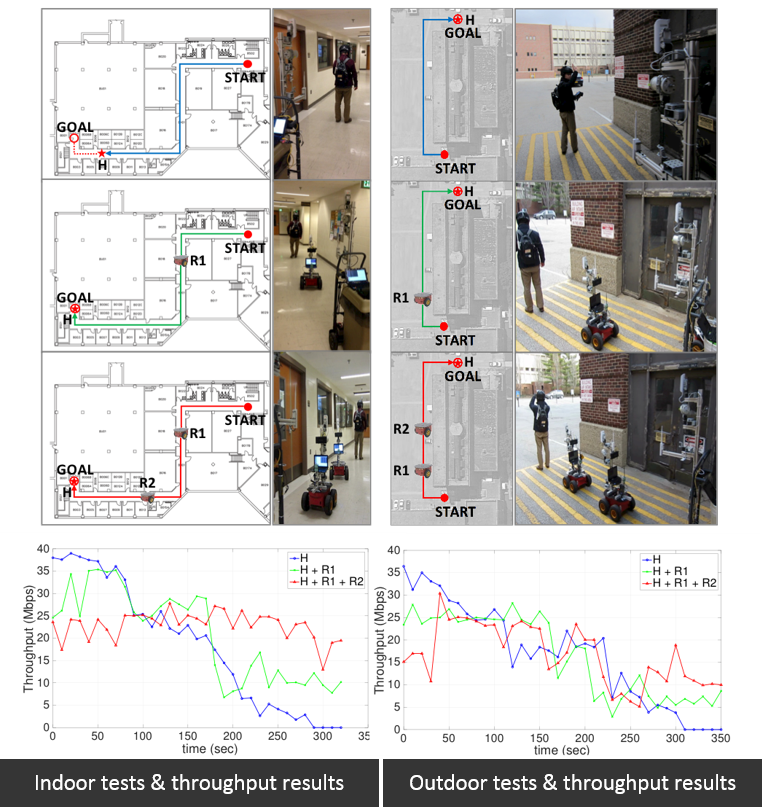
Description: In this research, we present
a directional antenna-based leader-follower robotic relay
system capable of building end-to-end communication in
complicated and dynamically changing environments. The
proposed system consists of multiple networked robots - one is
a mobile end node and the others are leaders or followers
acting as radio relays. Every follower uses directional
antennas to relay a communication radio and to estimate the
location of the leader robot as a sensory device. For bearing
estimation, we employ a weight centroid algorithm (WCA) and
present a theoretical analysis of the use of WCA for this
work. Using a robotic convoy method, we develop online,
distributed control strategies that satisfy the scalability
requirements of robotic network systems and enable cooperating
robots to work independently. The performance of the proposed
system is evaluated by conducting extensive real-world
experiments that successfully build actual communication
between two end nodes.
Grants: Purdue University
People: Sangjun Lee, Ramviyas Parasuraman
Selected
Publications:
- Byung-Cheol Min, Ramviyas Parasuraman, Sangjun Lee, Jin-Woo Jung, and Eric T. Matson, "A Directional Antenna based Leader-Follower Relay System for End-to-End Robot Communications", Robotics and Autonomous Systems, Vol. 101, pp. 57-73, March 2018. Download PDF, Download Video I, Download Video II
- Byung-Cheol Min, Eric T. Matson, and Jin-Woo Jung, “Active Antenna Tracking System with Directional Antennas for Enhancing Wireless Communication Capabilities of a Networked Robotic System", Journal of Field Robotics, Vol. 33, Issue 3, pp. 391-406, May 2016. Download PDF
Interactive Indoor Navigation Aid System for Visually Impaired People (2015 - 18)


Description: World Health Organization
(WHO) estimates that 285 million people in the world are
visually impaired, of whom 39 million are blind. Although
safe and independent mobility is a critical element of
modern life, traveling in unfamiliar environments can be
challenging and often daunting for visually impaired people
due to the lack of appropriate navigation aid tools. In
order to get familiarity with new places, visually impaired
people usually take many times of mobility training through
orientation & mobility instructors or their family.
However, this training is time consuming and expensive for
all the parties. Furthermore, it often appears to be
challenging for visually impaired people to memorize all the
steps to navigate new places independently. The objective of
this project is to develop improved and appropriate
navigation aid tools that will enable visually impaired
people to travel unfamiliar environments safely and
independently with minimal training and effort.
Grants: Purdue University
People: Yeonju Oh
Selected Publications:
- Yeonju Oh, Wei-Liang Kao, and Byung-Cheol Min, "Indoor Navigation Aid System Using No Positioning Technique for Visually Impaired People", HCI International 2017 - Poster Extended Abstract, Vancouver, Canada, 9-14 July, 2017. Download PDF, Download Video
Emergency and Non – Emergency Response Using Smartphone-based Indoor Localization (2016 - 17)

Description: The purpose of this study
is for a blind user to request help based on emergency and
non-emergency situation using indoor navigation application.
Usage of indoor navigation application is to serve the
purpose of sending the exact location of a blind user to the
responders when the blind user is in indoor settings. The
goal of the study is twofold. The first goal of this
research is to build an android application and achieve
accuracy of one meter or less using Wi-Fi signals inside the
building. The second goal of this study is to evaluate the
usefulness of providing the exact location i.e., room
number, floor, floor map and building name to the emergency
responders to reach the destination promptly. The main idea
behind this project is to evaluate, if providing exact
location of a user inside a building helps emergency or
non-emergency responders to reach location inside the
building quicker rather than searching entire building for
the victim. As a preliminary study, an accuracy of one meter
was achieved around 70 percent of the time in our test runs,
and this accuracy implies that we were able to send the
exact location of the blind user with one-meter accuracy to
the responders 70 percent of the times.
Grants: Purdue University
People: Manoj Penmetcha, Arabinda Samantaray
Selected
Publications:
- Manoj Penmetcha, Arabinda Samantaray, and Byung-Cheol Min, "SmartResponse: Emergency and Non-Emergency Response for Smartphone based Indoor Localization applications", HCI International 2017 - Poster Extended Abstract, Vancouver, Canada, 9-14 July, 2017. Download PDF
Examine the Potential of Robots to Teach Emotional Concepts (2015 - 16)
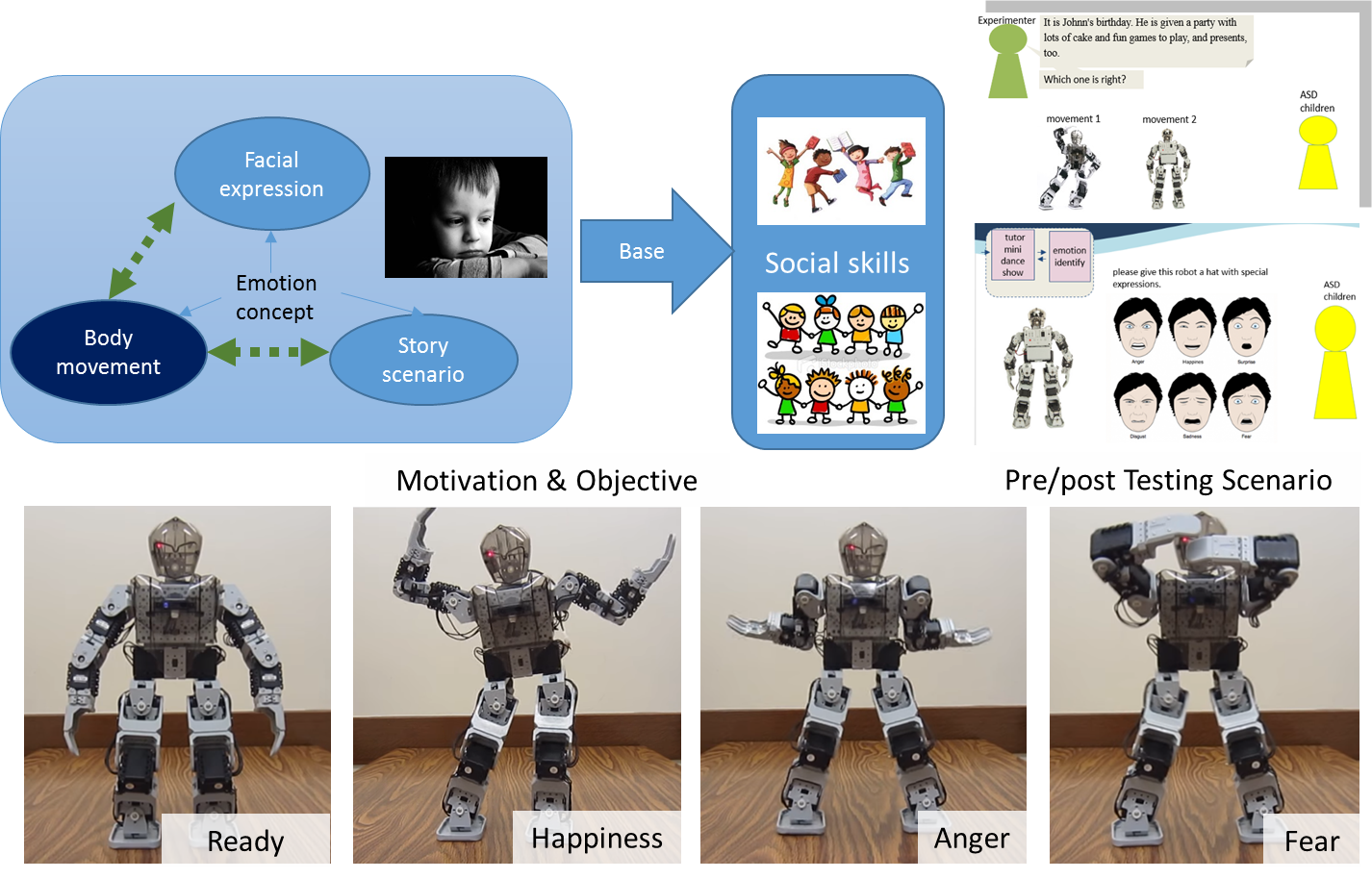
Description: Autistic people is a
special group who have impaired ability in social
interaction, social communication and imagination. Several
approaches have been used to help them, among which humanoid
robot is emerging as a new tool to teach them recently,
since it could offer more simplified physical features and
controllable environment which is preferred by autistic
children. At the same time, a robot could offer a
human-friendly conversational environment which is
appropriate to emotion and social skills learning. This
project is trying to design a set of robot body movements
which is supposed to express different emotions and a
robot-mediated instruction prototype to explore the
potential of robots to teach emotional concepts to autistic
children.
Grants: Purdue University
People: Huanhuan Wang, Pai-Ying Hsiao
Selected Publications:
- Huanhuan Wang, Pai-Ying Hsiao, and Byung-Cheol Min, "Examine the Potential of Robots to Teach Autistic Children Emotional Concepts", The Eight International Conference on Social Robotics (ICSR), Kansas City, USA, Nov. 1-3, 2016. Download PDF
Learn Braille Device (2015 - 16)
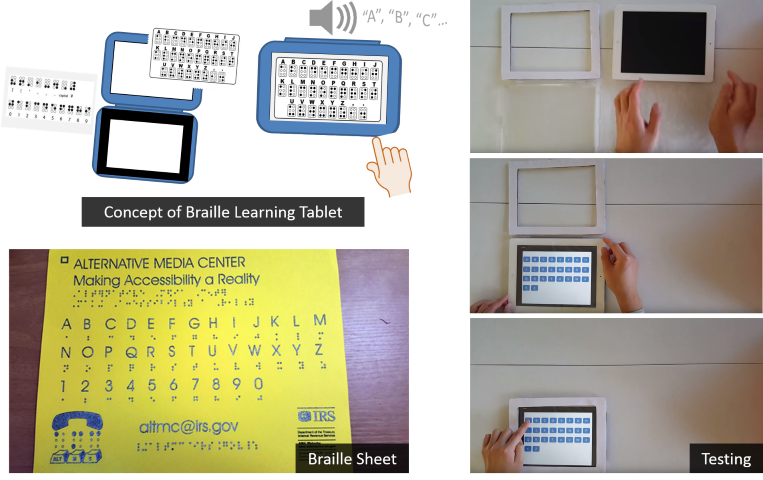
Description: Braille is a language
that was developed with the sole intention of providing a
medium for users who are blind or have low-vision to
understand text the same way humans read and write text.
Due to the loss of at least one sensory input, this
language systems relies on a user’s ability to touch and
feel. However, historically, in order to learn braille,
the user must rely on additional help to understand how to
obtain information from braille. Especially in this era
when there are less teaching professionals qualified to
teach braille. Therefore, we present a novel approach that
provides an alternative to helping users who are blind or
low-blind disabilities to learn braille by use of
affordable technologies.
Grants: Purdue University
People: Wei Kao, Robert Hinh
Adaptive Learning System in Language based Environment for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (2015 - 16)
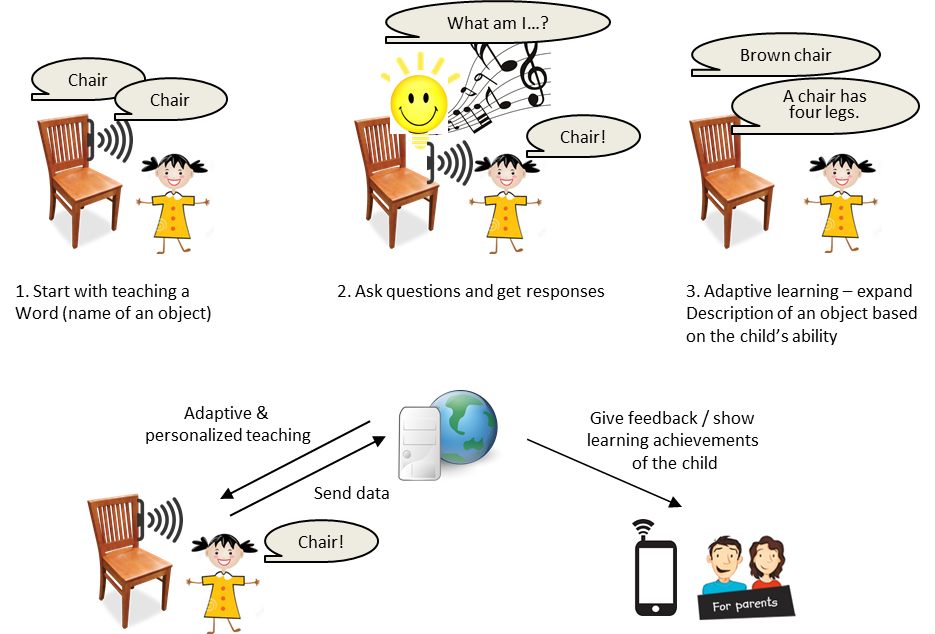
Description: Autism spectrum
disorder (ASD) is one of the most significant public
health concerns in the United States and also
worldwide. Children with ASD are often lack in verbal
ability. Even though early interventions can improve
it greatly, high cost and difficult access to special
education services challenge families with a child
with ASD. This research study proposes a technical
methodology that can be easily deployed in a daily
environment of children with ASD and teach language to
them with low cost, based on embedded devices and
semantic information which can be extended to a
cyber-physical system in the future. This method will
provide verbal descriptions of objects and also adapt
the level of descriptions to the child's learning
achievements. This project is collaborated with the M2M
Lab at Purdue University.
Grants: Purdue University
People: Sangmi Shin
Selected
Publications:
- Sangmi Shin, Byung-Cheol Min, Julia Rayz, and Eric T. Matson, "Semantic Knowledge-based Language Education Device for Children with Developmental Disabilities", IEEE Robotic Computing (IRC) 2017, Taichung, Taiwan, April 10-12, 2017. Download PDF
Establishment of End-to-End Wireless Network with Mobile Robots (2013 - 16)
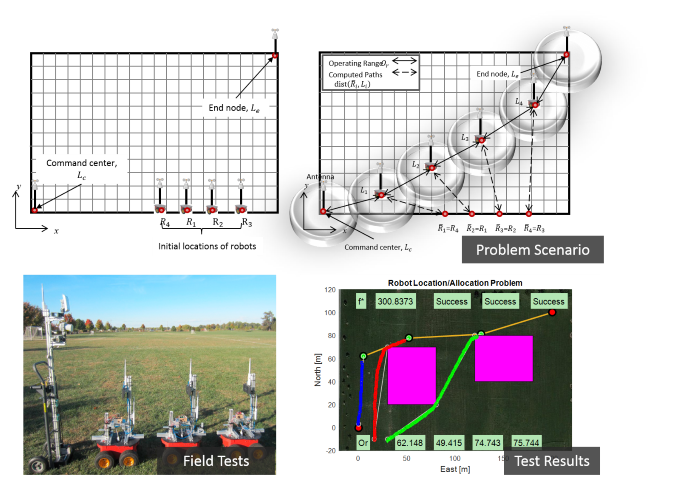
Description: In this
research we tackle the fundamental problem of
finding the optimal location and allocation of
mobile robots in an application of the
establishment of an immediate end-to-end
communication. Often this is called the
multi-robot deployment problem in networked
robotics. To this end, we formulate an
end-to-end communication problem, in a general
optimization form, with constraints that
consider the operation of robots and the types
of antennas. Additionally, constraints on the
propagation of radio signals and infeasible
locations of robots within physical obstacles
are also taken into consideration for a dense
space. To solve the optimization problem we
explore the use of evolutionary optimization
techniques such as Genetic Algorithm (GA) and
Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO).
Grants: Purdue University
People: Sangjun Lee
Selected Publications:
- Byung-Cheol Min, Yongho Kim, Sangjun Lee, Jin-Woo Jung, and Eric T. Matson, “Finding the Optimal Location and Allocation of Relay Robots for Building a Rapid End-to-end Wireless Communication", Ad Hoc Networks, Vol. 39, Issue 15, pp. 23-44, March 2016. Download PDF
